Animal Behavior Patterns – Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.1 Basic Behaviors Behaviors occur in response to internal or external stimuli. What influences behavior? Behavior arises from the interaction of genetic and behavioral-based behaviors.
Chapter 31 Animal Behaviors 31.1 Evolutionary Behaviors Basic Behaviors What Causes a Response to a Stimulation The answer is usually found by studying the internal biology of animals. What are the benefits of that attitude?
Animal Behavior Patterns

5 Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.1 Basic Behaviors Congenital Behavior A behavior is called innate if the same behavior is commonly observed among many individuals in a population, despite different environments. . Her worm behavior
Infographic: Animal Sleep Patterns & Nocturnal Activity
6 Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.1 Basic Behaviors Constant Behavioral Patterns Stimulation causes a congenital response that the animal cannot control and is not directly affected by environmental conditions or past experiences.
7 Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.1 Basic Behaviors studied Behaviors learned from behaviors that result from interactions of innate behaviors and past experiences in a particular environment.
8 Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.1 Basic Behavior Over time, animals may learn that significant stimuli deserve little attention. Habit is to reduce the animal’s response after repeated exposure to stimuli that have no positive and negative effects.
Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.1 Basic Behavior Classical Conditions Classical conditions occur when a relationship is made between two different types of stimuli.
Patterns In Nature Institute
10 Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.1 Basic Behaviors Operating Conditions In animal operating conditions learn to associate their responses to stimuli with rewards or punishments. For example, if a bird eats a butterfly that tastes bad, it associates the color of the butterfly with its flavor and avoids all butterflies that have that color. See the type of behavior
11 Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.1 Basic Behaviors Some animals make social connections to the first objects they see in life. Other animals reflect the chemical composition of the water in which they are hatched.
12 Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.1 Basic Cognitive Behavior Cognitive behavior is the thinking, reasoning, and processing of information required to understand complex concepts and solve problems. People show an understanding attitude when solving problems, making decisions and planning for the future.

Chapter 31 Animal Behaviors 31.2 Ecological Behaviors Types of Behavior Animals that have complex behaviors survive and reproduce because they inherit a gene that enables them to thrive in a specific environment.
Ai Tool
Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.2 Ecological Behavior Competitive Behavior Competition for food, space, mates, and other resources occurs between individuals within a population. Competitive behavior allows individuals to establish control or control over territory or resources.
15 Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.2 Ecological Behavior Aggressive behavior Threats or interactions between two individuals of the same species are called aggressive behaviors. Aggressive behavior usually does not cause injury or death to any individual.
Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.2 Ecological Behavior Control Hierarchy Some animals that live in groups form a control hierarchy where the top animals can access resources without conflict with other animals in the group. This classification system reduces hostile behavior between animals.
Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.2 Ecological Behavior Territorial Behavior Terrible behaviors include verbal signals such as bird calls and chemical signals such as geese urine. Territories are usually protected by men to increase their chances of having enough food, colleagues and their offspring.
Essentials Of Animal Behavior (short Summary)
18 Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.2 Ecological Behaviors Feeding Behavior Successful rearing means getting the nutrients needed while avoiding predators and food poisoning. Natural selection favors individuals whose breeding behavior uses the least energy to get the most amount of energy.
19 Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.2 Ecological Behavior Migration Behavior Animals that use migratory behavior increase their chances of survival by finding new food sources.
Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.2 Ecological Behavior Biological rhythms Circadian rhythms are cycles that occur on a daily basis, such as sleep and wakefulness. Many animals have an internal clock that maintains the daily rhythm of their sleep / wake cycle.

Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.2 Ecological Communication Behavior Communication behavior is important for animal survival and reproductive success. Animals have many different communication behaviors.
Animal Behavior Chaptest
Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.2 Ecological Behavior Pheromones Some animals interact by releasing highly specific chemicals called pheromones. These chemicals are specific. Pheromones are often used to transmit reproductive messages between men and women.
Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.2 Ecological Behavior Communication, auditing, echoing, shouting, and barking are just a few examples of phonetic communication. Language is a type of phonetic communication in which animals use sound organs to form groups of sounds that have a common meaning.
Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.2 Ecological Behavior Behavior Judgment Animals engage in paired behaviors to attract mates. Women often choose to mate with men who are bigger and healthier than others.
25 Chapter 31 Animal Behaviors 31.2 Ecological Behaviors Parenting When parents provide care for their offspring in the early stages of development, they are engaged in upbringing. This includes feeding, protection, and skills necessary for survival. Species that spend time breeding often produce fewer offspring than non-breeding animals.
Summary Animal Behavior Chapter 1 11
26 Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.2 Ecological Behavior Altruistic Behavior Animals can practice behaviors that benefit other individuals at their own expense. For example, a colony of naked rats feeds, protects the queen, and swims around the queen to keep her offspring warm.
27 Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.2 Ecological Behavior Selection of Relatives According to the concept of relative selection, loyalty behaviors evolve as the number of genes that are common in the population increases.
Animal Behavior Chapters Resource Menu Chapters Diagnostic Questions Test Questions Evaluation Test Standards Practice Test biologygmh.com Glencoe Biology Transparency Film Image Banking Vocabulary Animation Click the hyperlink to view the corresponding Masu lesson.

Chapter 31 Animal Behavior Chapter Diagnostic Questions Which of the following is an example of a response to external stimuli? Salmon that swims up to the eggs that sing during the mating season
Buy Animal Behavior: Concepts, Methods, And Applications Book Online At Low Prices In India
Chapter 31 Animal Behavior Chapter Diagnostic Questions What types of behaviors occur only during animal sensitivity?
Chapter 31 Animal Behavior Chapter Diagnostic Questions Which of the following is not an elephant communication medium?
Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.1 Form Questions What are the terms for environmental change that affect the activities of living things?
Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.1 Form Questions What are the main questions about animal behavior that scientists have tried to answer, how are behaviors based on genetics or experience, how do animals respond to the same stimuli? What is the relationship between motivation and response?
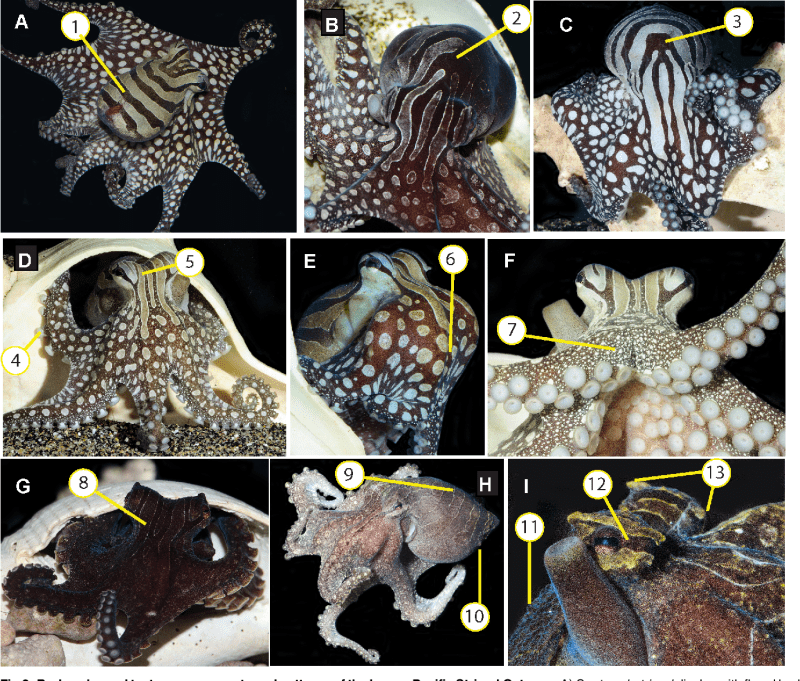
Pdf] Behavior And Body Patterns Of The Larger Pacific Striped Octopus
Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.1 Form Questions How do scientists determine why animals respond to a specific stimulus? They examine the internal biology of animals. They study the nature of animal reactions. They study the benefits of specific activities. They test different stimuli and measure responses.
Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.1 Form Questions Which one best determines congenital behavior?
Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.1 Questions in True / False Form Experimental evidence shows that animals other than humans can also think and solve problems.

Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.2 Question Form: What are the similarities between aggressive behavior and territory? They are willing behaviors. These are competitive behaviors. They are based on biological rhythms. They need phonetic communication.
Neurobiology Of Behavior #1
CHAPTER 31 ANIMAL BEHAVIOR 31.2 Form questions What causes the first migration of birds?
Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.2 Form Questions What maintains the daily rhythm of the sleep / wake cycle in many animals? Behavior hibernation, temperature change, internal clock, feeding and water
Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.2 Question Which form of communication has the shortest range of visual signals?
Chapter 31 Animal Behavior 31.2 Form Questions What are some other ways to describe the behavior of an honest animal? Communal Commensal
Animal Behavior Evolution
Chapter 31 Questions Assessing Animal Behavior Learned Behavior What does a police horse show when it is no longer affected by noise and traffic?
Chapter 31 Animal Behavior Chapter Evaluation Questions What are the advantages of animals that use phonetic communication rather than pheromones? A: Phonetic messages travel faster than chemical messages, so it is more likely that the message they receive will be more sexual.
Chapter 31 Animal Behaviors Chapter Evaluation Questions Which of the following does not occur in a group of animals under a controlled hierarchy? Animals are classified from highest to lowest. Higher-ranking animals have access to resources. Fighting animals

Cheaters behavior patterns, ptsd behavior patterns, bipolar behavior patterns, narcissistic patterns of behavior, behavior patterns of bipolar disorder, behavior patterns, changing behavior patterns, how to change negative behavior patterns, stalking behavior patterns, how to change behavior patterns, alcoholic behavior patterns, abusive behavior patterns
- Pet-friendly Weekend Getaways - August 13, 2024
- Dog-friendly Road Trips - August 13, 2024
- Top Dog-friendly Resorts - August 13, 2024